Official Report: The Effects of Phonk Music on the Brain and Mental Health
Report Prepared by an Independent Journalist Specializing in Science and Culture
Date: January 07, 2026

Typical visual aesthetic associated with Drift Phonk music (dark, intense, bass-heavy).
Executive Summary
Phonk, an emerging music genre characterized by heavy distorted bass, aggressive rhythms, and often dark atmospheres, has gained massive popularity among adolescents and young adults through platforms like TikTok. While some listeners report stimulating effects (increased focus or adrenaline), scientific studies on aggressive music and low-frequency bass indicate potential risks: heightened aggressive thoughts, mental rumination, hearing damage, and interference with brain development in youth. This report synthesizes available scientific evidence to highlight the dangers of excessive listening.
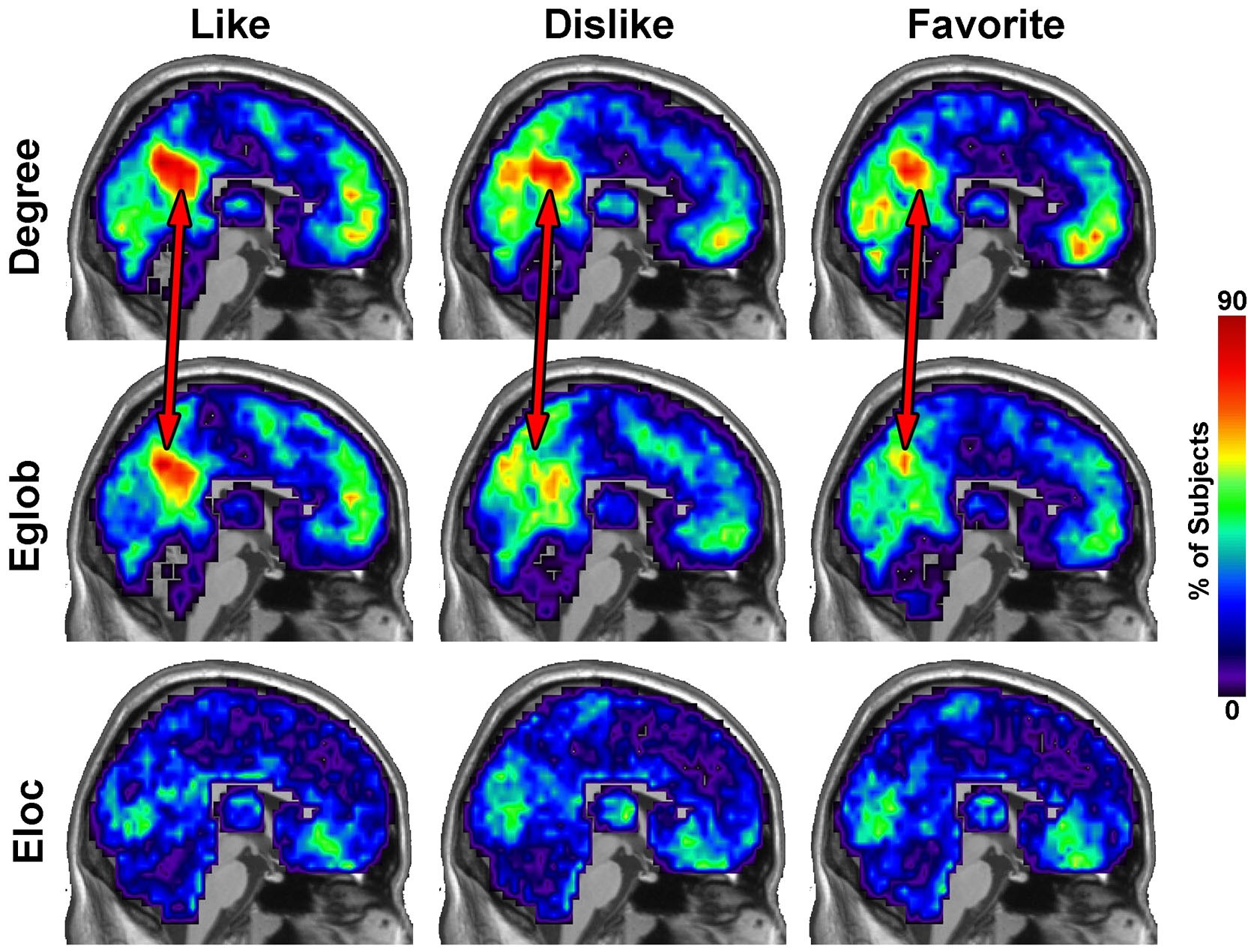
Scientific illustration showing how music preferences affect functional brain connectivity (Source: Nature).
Introduction
Phonk (particularly "drift phonk") relies on intense sonic elements: overdriven 808 bass, distorted cowbells, and repetitive samples drawn from 1990s Memphis rap. These features stimulate the nervous system, releasing dopamine and adrenaline, but prolonged exposure may lead to negative long-term effects. This document examines these impacts on the brain, drawing from neuroscience and music psychology research.

Example of Phonk music playlist featuring heavy cowbell and bass elements.
Sonic Characteristics of Phonk and Brain Interaction
Low-frequency bass: Sounds below 100 Hz physically vibrate the body and activate brain reward centers.
Aggressive rhythms: These alter brain waves, increasing alertness (beta waves).
These elements can induce immediate excitement, but prolonged exposure carries risks.

Illustration of low-frequency sound waves and vibrations, similar to the heavy bass in phonk.
Documented Negative Effects
1. Increased Aggression and Hostile Thoughts
Music with aggressive tones or violent themes amplifies hostile thoughts and feelings of aggression, especially in adolescents. Meta-analyses show that repeated exposure to violent lyrics or intense sounds contributes to more aggressive personality traits. Although phonk is often instrumental, its intense tone and cultural associations (toxic "sigma" content) can produce similar effects.

How aggressive music can influence mood and behavior in the brain.
2. Rumination and Mental Health Impacts
Listening to dark or aggressive music promotes rumination (repetitive negative thought cycles), worsening anxiety and depression. This is particularly risky for young people, where excessive exposure can trap individuals in negative emotions.
3. Hearing Damage from Heavy Bass
Contrary to common belief, low-frequency bass is dangerous: it causes cumulative hearing loss and impairs higher cognitive functions (reasoning, calculations). Listening at high volumes (headphones or speakers) accelerates these effects.

Warning about hearing damage from loud music and headphones.
4. Vulnerability in Adolescents
The adolescent brain continues maturing until approximately age 25. Intense music can interfere with this development, increasing impulsivity and negative emotions.
| Negative Effect | Primary Mechanism | At-Risk Populations | Scientific Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aggressive thoughts | Activation of emotional pathways by fast rhythms | Impulsive adolescents | APA studies on violent lyrics |
| Mental rumination | Reinforcement of negative cycles by dark tone | Youth with anxiety/depression | Research on sad/aggressive music |
| Hearing damage | Excessive vibration of hair cells | High-volume listening | Studies on low-frequency noise |
| Developmental disruption | Impact on neuronal plasticity | Adolescents (<25 years) | Developmental neuroscience |
Nuances and Positive Aspects
In moderation, some effects can be positive: adrenaline boost for motivation or improved focus (similar to "lo-fi on steroids"). However, risks outweigh benefits with excessive listening.
Recommendations
- Moderate volume and listening duration.
- Diversify music genres.
- Parents and educators: monitor signs of mood changes or dependency.
- Consult professionals for hearing or mental health concerns.
Conclusion
Phonk is not inherently harmful, but its aggressive characteristics and intense bass present proven brain risks, especially for young people. A balanced approach is essential. Specific studies on phonk would help deepen these observations.
Sources: Synthesis of published studies (APA, PMC, ScienceDirect) and cultural analyses. This report is for informational purposes; consult experts for personalized advice.
Commentaires
Enregistrer un commentaire